Exec System Call
Arguments: File Name (String) of the executable file (which must be of XEXE format)
Return Value:
| -1 | File not found or file is of invalid type |
Description: Exec destroys the present process and loads the executable file given as input into a new memory address space. A successful Exec operation results in the extinction of the invoking process and hence never returns to it. All open instances of file and semaphores of the parent process are closed. However, the newly created process will inherit the PID of the calling process.
The data structures that are modified in this system call are Process Table, Memory Free List, Disk Free List, Open File Table, Semaphore Table, System Status Table, Resource Table and the Disk Map Table.
The mode flag in the Process Table has to be set to Kernel mode when the process enters the system call and reset before exiting from the system call.
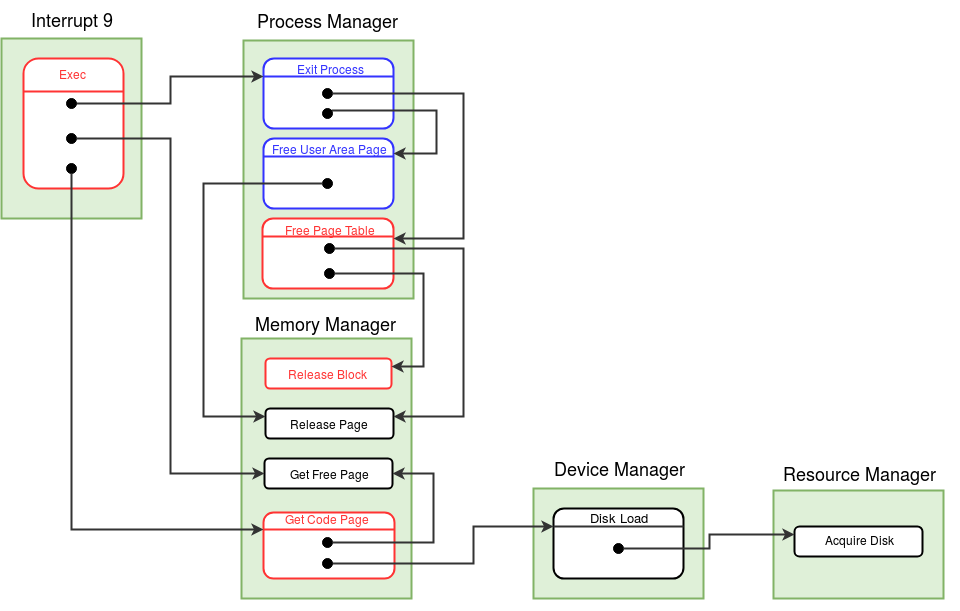
Algorithm:
Set the MODE_FLAG in the process table entry to 9 indicate that the process is in exec system call. //Switch to the Kernel Stack. see kernel stack management during system calls Save the value of SP to the USER SP field in the Process Table entry of the process. Set the value of SP to the beginning of User Area Page. /* Check for the file entry in Inode Table. */ If filename is invalid, return -1. If file not found in system or file type is not EXEC, return -1 Call the exit_process() function in the Process Manager Module to deallocate resources of the current process. Reacquire the same User Area Page of the old process manually by incrementing the Mem Free List and decrementing MEM_FREE_COUNT in the System Status Table. /* exit_process() in the previous step deallocated the user area page, and hence we immediately reclaim the page for loading the new program. Since the page storing the kernel context has been de-allocated, it is unsafe to invoke the memory manager module for allocating a fresh user area page (why?) */ Set SP to User Area Page Number * 512 - 1 /* Start fresh in the new kernel stack */ Initilize the Per-process Resource Table by setting all entries to -1. In the Process Table entry of the current process, set the Inode Index field to the index of Inode Table entry for the file and set the state as RUNNING. Acquire two memory pages for user stack by invoking the get_free_page() function in the memory manager module. Obtain the disk block number of the first code page from the inode entry of the file passed as argument. Load the first code page into memory by invoking the get_code_page() function in the Memory Manager module. Set the Page Table and Disk Map Table entries of the process.Set the Page Table entries for library. Set the valid bit to 1 and write bit to 0. /* Since the ExpL compler uses the library for even basic operations like read/write, the library flag is ignored, and we link the library to all loaded programs */ Invalidate the page table entries for heap. /* Memory will be allocated when page fault occurs */ Set the page table entry for the first code page to the page loaded eariler. Set it's valid bit to 1 and write bit to 0. Other code pages are set to invalid and unreferenced. Set the page table entry for the stack page to the pages found earlier. Set the valid bit and write bit to 1. Set the code pages in the Disk Map Table to the Block numbers by refering to the Inode Table. Other fields are set to -1.Obtain the entry point IP value from the header of the new process and set it to the beginning of user stack(logical address 4096). Set SP to the logical address of the user stack. Set the MODE_FLAG in the process table entry to back to 0. ireturn from system call to newly loaded process. Note: At each point of return from the system call, remember to reset the MODE FLAG and switch back to the user stack.